When it comes to the world of chemistry and ions, the term "NO3 charge" holds a significant place in understanding molecular interactions and the behavior of compounds. NO3, known as the nitrate ion, is an essential component in various chemical reactions and plays a pivotal role in scientific disciplines such as environmental science, biology, and industrial applications. Its charge directly influences its reactivity, stability, and the way it interacts with other elements and compounds in nature.
Delving into the concept of the NO3 charge is crucial for students, researchers, and professionals alike. This ion, with its unique characteristics and properties, is not only vital in laboratory experiments but also critical in real-world contexts, such as water treatment, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Understanding the charge of NO3 helps explain how it combines with other substances to form nitrates, which are commonly found in fertilizers and natural ecosystems.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about the NO3 charge, including its significance, how it’s formed, its structural composition, and much more. Whether you’re a chemistry enthusiast, a student preparing for exams, or someone curious about the role of ions like NO3 in our daily lives, this article will provide all the insights you need. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
- What Is NO3 Charge?
- How Is NO3 Charge Formed?
- Why Is NO3 Charge Negative?
- Chemical Structure of NO3
- Importance of NO3 in Chemistry
- What Are Common Compounds Containing NO3?
- Role of NO3 in Environmental Science
- How Does NO3 Charge Affect Chemical Reactions?
- Applications of NO3 in Everyday Life
- Difference Between NO3 and Other Ions
- How to Calculate NO3 Charge?
- What Happens When NO3 Interacts with Other Elements?
- Health and Safety Concerns Related to NO3
- Interesting Facts About NO3
- Frequently Asked Questions About NO3 Charge
What Is NO3 Charge?
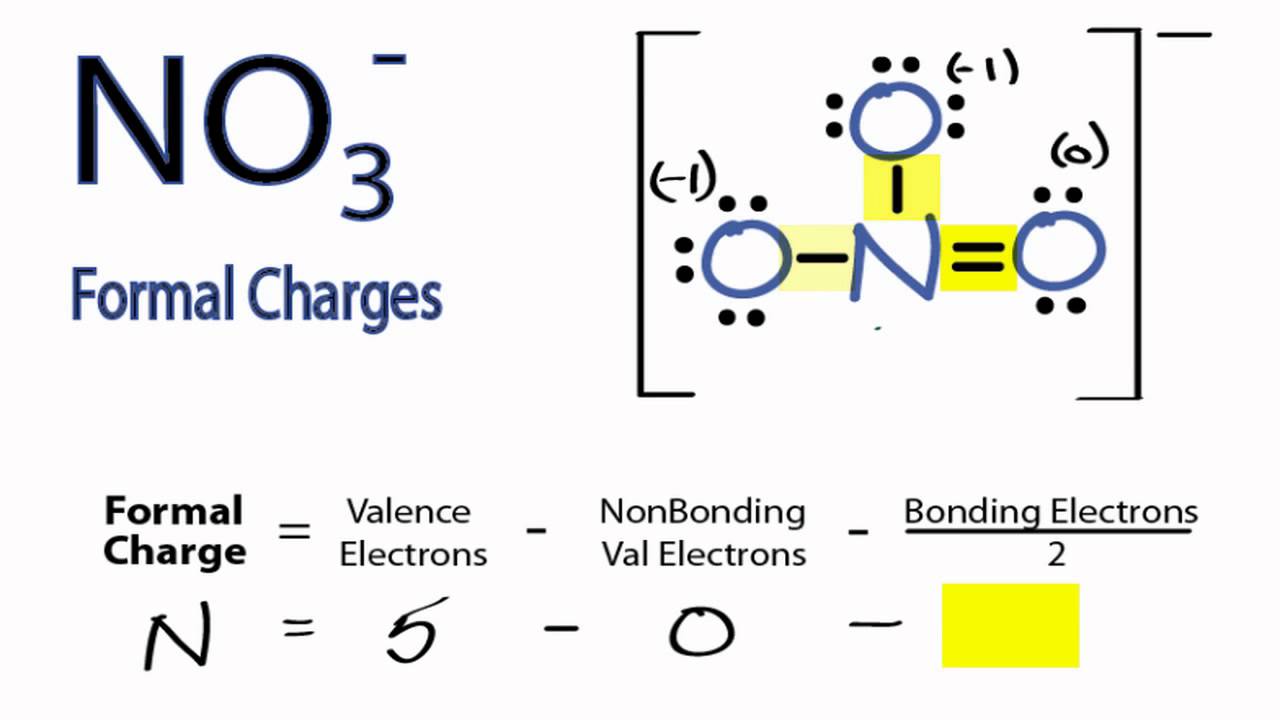
The NO3 charge refers to the electrical charge associated with the nitrate ion (NO3). In its stable state, NO3 carries a negative one (-1) charge, making it an anion. This charge arises because the nitrate ion contains one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms, where the total number of electrons exceeds the total number of protons, resulting in a negative charge.
How Is NO3 Charge Formed?
NO3 charge is formed during a chemical process where a nitrogen atom bonds with three oxygen atoms. The overall structure consists of covalent bonds between nitrogen and oxygen atoms, but the ion also gains an extra electron, leading to its negative charge. This additional electron originates from external sources, such as during the dissociation of nitric acid (HNO3) in water.
Why Is NO3 Charge Negative?
The NO3 charge is negative because the nitrate ion gains an extra electron during its formation. This extra electron is not balanced by a corresponding proton, resulting in an overall negative charge. The negative nature of NO3 plays a crucial role in its ability to form ionic bonds with positively charged ions like sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+).
Chemical Structure of NO3
The nitrate ion (NO3) has a trigonal planar structure, with the nitrogen atom at the center and three oxygen atoms arranged symmetrically around it. The nitrogen atom forms double bonds with one oxygen atom and single bonds with the other two, while the negative charge is delocalized across the entire ion, contributing to its stability.
Importance of NO3 in Chemistry
In the realm of chemistry, NO3 is a fundamental ion that plays a significant role in various chemical reactions. Its ability to form compounds like nitrates is essential for processes such as nutrient cycling in ecosystems, industrial manufacturing, and the synthesis of fertilizers. Understanding the NO3 charge is key to predicting its behavior in these contexts.
What Are Common Compounds Containing NO3?
Some common compounds containing the NO3 ion include:
- Sodium nitrate (NaNO3) – used in food preservation and fertilizers
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3) – used in fireworks and fertilizers
- Calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) – used in agriculture to improve soil nutrition
Role of NO3 in Environmental Science
The NO3 ion plays a critical role in environmental science, particularly in the nitrogen cycle. It serves as a vital nutrient for plant growth but can also contribute to environmental issues such as water pollution and eutrophication when present in excessive amounts. Monitoring and managing NO3 levels in soil and water are crucial for sustainable agriculture and ecosystem health.
How Does NO3 Charge Affect Chemical Reactions?
The negative charge of NO3 allows it to readily interact with positively charged ions, forming ionic compounds. This behavior is essential in various chemical reactions, including those involved in fertilizer production, water purification, and explosive manufacturing. The NO3 charge also influences the solubility and stability of these compounds.
Applications of NO3 in Everyday Life
NO3 has numerous applications in daily life, including:
- Fertilizers: Providing essential nutrients for plants
- Food preservation: Used in curing meats to inhibit bacterial growth
- Pyrotechnics: Key ingredient in fireworks and explosives
Difference Between NO3 and Other Ions
While NO3 is a negatively charged anion, it differs from other ions in terms of its composition, structure, and reactivity. For instance, unlike chloride ion (Cl-) or sulfate ion (SO4^2-), NO3 contains a nitrogen atom, which gives it unique properties and applications in both organic and inorganic chemistry.
How to Calculate NO3 Charge?
Calculating the NO3 charge involves evaluating the total number of protons and electrons in the ion. In the case of NO3, the nitrogen atom has 7 protons, each oxygen atom contributes 8 protons, and there is one additional electron, resulting in a net negative charge of -1.
What Happens When NO3 Interacts with Other Elements?
When NO3 interacts with other elements, it forms various compounds, such as nitrates and nitrites. These interactions are governed by the ion's negative charge, which attracts positively charged ions like sodium (Na+) or calcium (Ca2+). The resulting compounds have diverse applications, ranging from agriculture to industrial processes.
Health and Safety Concerns Related to NO3
While NO3 is essential in many applications, excessive exposure can lead to health and environmental concerns. High levels of nitrates in drinking water, for example, can cause methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome) in infants. Proper management and monitoring of NO3 levels are critical to mitigate these risks.
Interesting Facts About NO3
Did you know?
- The NO3 ion is a key player in the nitrogen cycle, which is essential for life on Earth.
- Nitrates are naturally present in vegetables like spinach and beets.
- Explosives like dynamite often contain nitrate compounds due to their reactivity.
Frequently Asked Questions About NO3 Charge
Here are some common queries about the NO3 charge:
- Is NO3 always negatively charged? Yes, in its stable ionic form, NO3 always carries a -1 charge.
- Can NO3 exist without a charge? No, NO3 in its ionic form always has a charge due to its electron configuration.
- What industries rely on NO3? Agriculture, food preservation, and pyrotechnics are some industries that heavily use NO3-based compounds.
You Might Also Like
Understanding Your Location: What Country Am I In?Transform Your Space With A Functional And Stylish Small Vanity
Unveiling The Fascination Of Hei Hei: A Unique Insight
Understanding Isotonic Solution: A Comprehensive Guide
Is Rawhide Bad For Dogs? Uncover The Truth Behind This Popular Treat
Article Recommendations
- 2 Actors Died Yesterday
- Kash Patel Wife
- Exploring The World Of Mkvmoviespoint Everything You Need To Know